Cerebral Salt Wasting Treatment
Cerebral salt wasting treatment. Cerebral lesion excess renal loss of Na and Cl-cerebral lesions. Cerebral salt wasting CSW or more appropriately renal salt wasting RSW is a syndrome with a controversial history that evolved from a misrepresentation of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone SIADH to acceptance as a distinct entity. Hyponatremia may occur due to cerebral salt wasting syndrome or syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone SIADH.
Also now known as renal salt wasting. Cerebral salt wasting CSW is another potential cause of hyponatremia in those with CNS disease particularly patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. All other monitoring and documentation per NeuroICU protocol.
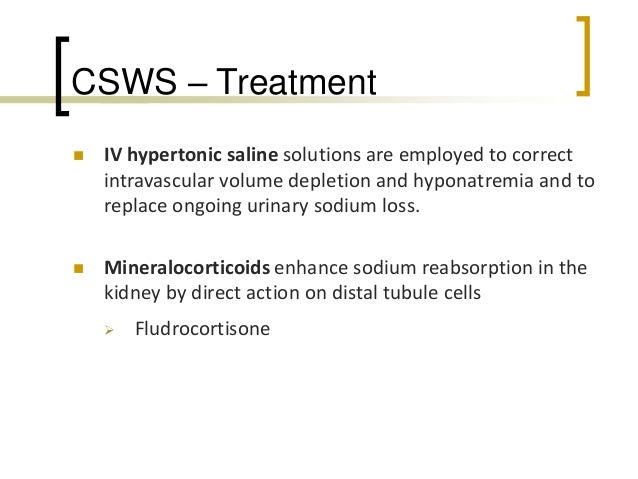
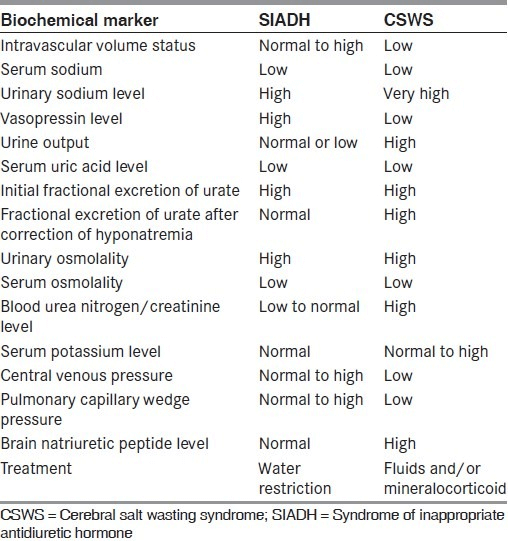
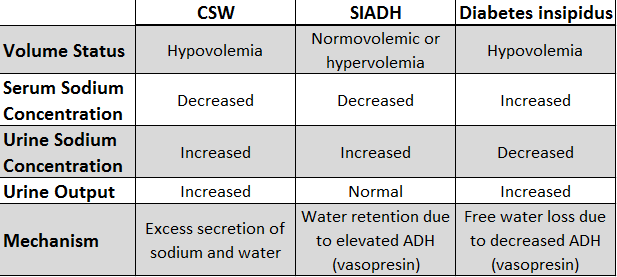
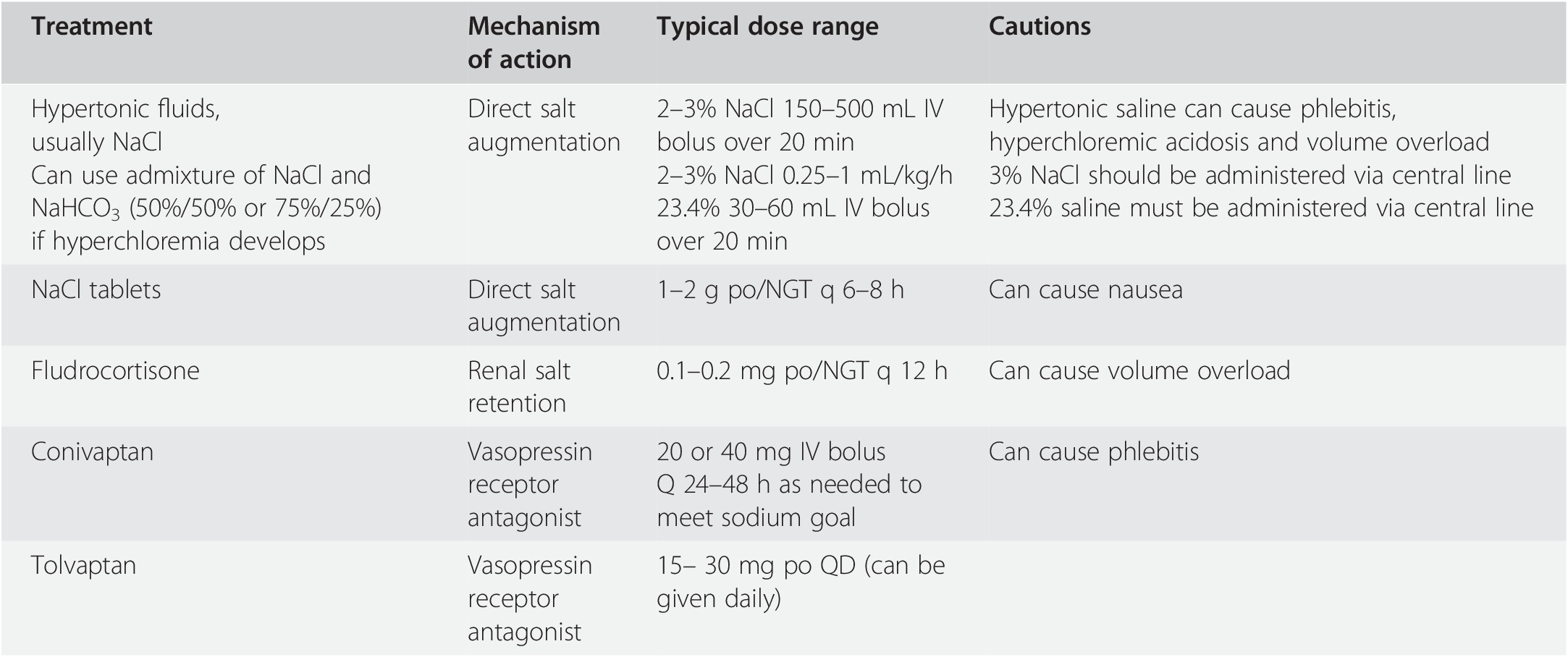
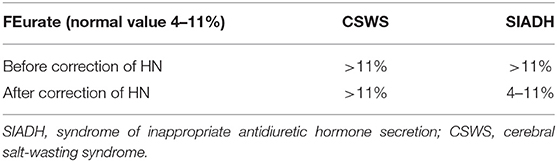
It is important to distinguish between cerebral salt wasting and SIADH as the 2 are treated with opposite treatment strategies. 1 Most patients with hyponatremia with normal renal function were initially attributed to the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone SIADH. Therapy for CSW includes volume repletion with isotonic saline and oral salt replacement for the duration of symptoms usually 3-4 weeks.
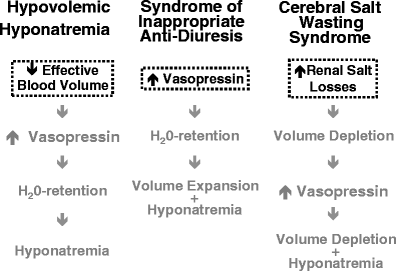
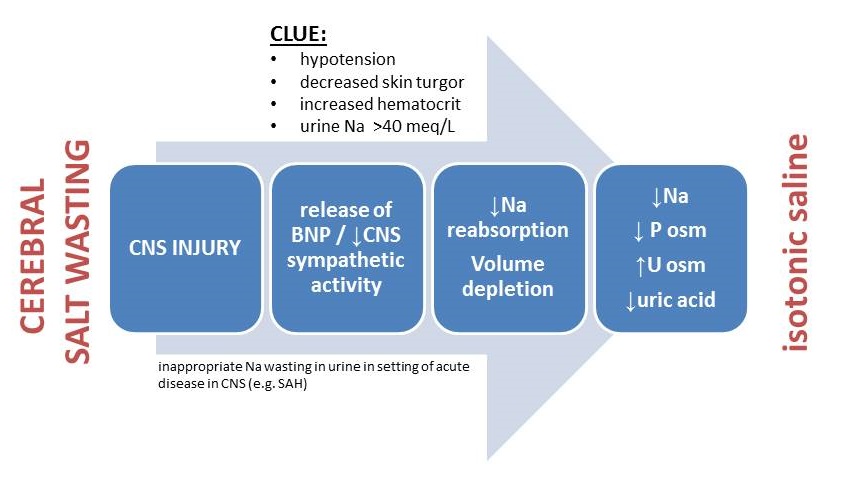
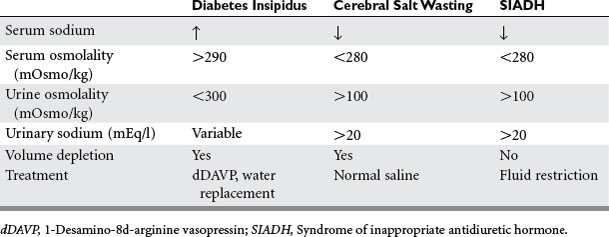
Cerebral salt wasting CSW is defined as the renal loss of sodium because of intracranial diseases leading to hyponatremia excessive natriuresis and volume depletion that responds to volume and salt replacement. However some authorities contend that CSW does not really exist and. Pathophysiology diagnosis and treatment Cerebral salt wasting CSW is a syndrome of hypovolemic hyponatremia caused by natriuresis and diuresis.
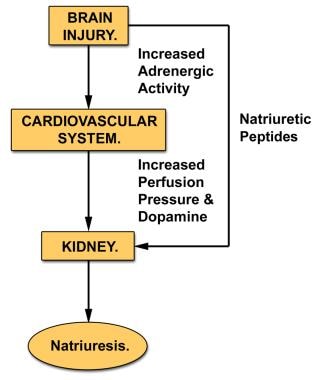
The proper treatment fluid and electrolyte resuscitation versus free water restriction requires an assessment of the patients volume status. Exact aetiology is unclearincreased adrenergic activity increased natriuretic peptides increased perfusion pressure increased dopamine. A vital clinical characteristic of patients affected by cerebral salt-wasting syndrome is that the aforementioned manifestations tend to respond positively to volume and sodium replacement.
Once the patient is stabilized enteral. Central venous pressure via a central venous catheter OR pulmonary artery occlusion pressure via a pulmonary artery catheter 2. 1 2 CSW is defined as the renal loss of sodium leading to hyponatremia and extracellular fluid volume loss.
Serum Na every 2 hrs 3. Cerebral salt wasting CSW was first proposed in 1950 to explain the natriuresis and hyponatremia that sometimes accompany intracranial disease.
Serum Na every 2 hrs 3.
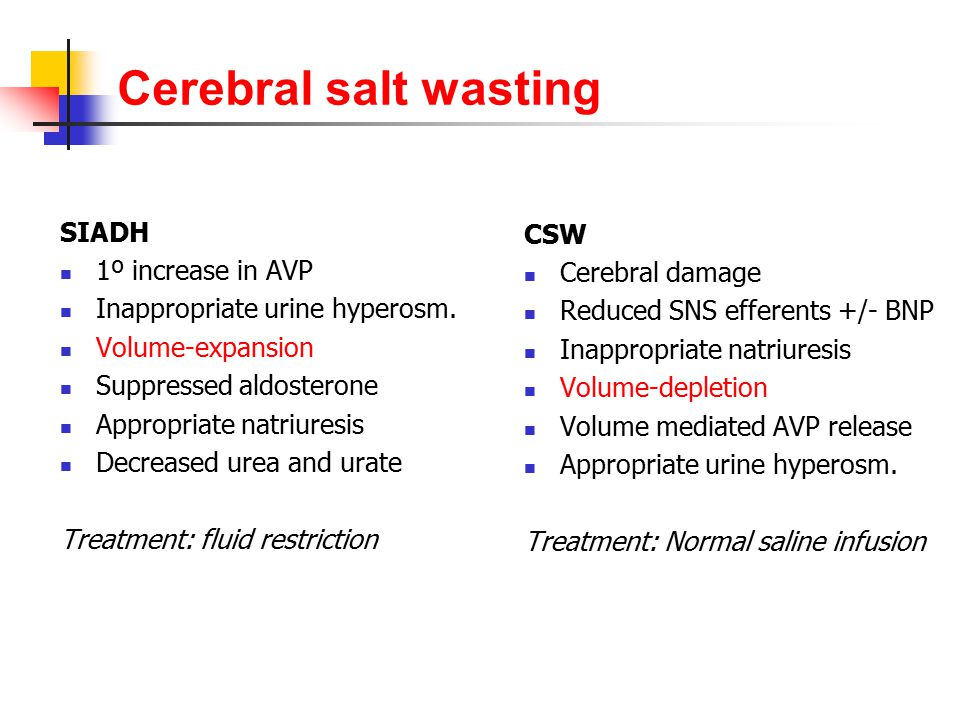
For cerebral salt wasting the patient is given fluids and sodium supplementation. 3 Water and salt supplementation is the primary therapy for CSW whereas water restriction is the primary treatment. Adequate volume repletion will remove the stimulus for ADH secretion resulting in dilute urine. Serum Na every 2 hrs 3. If the patient truly had cerebral salt wasting they would suffer hypovolemic and the SIADH treatment modalities would be detrimental by exacerbating the hypovolemia. Successful Treatment of Adult Cerebral Salt Wasting With Fludrocortisone Acid Base Electrolytes Fluids JAMA Internal Medicine JAMA Network. Also now known as renal salt wasting. Pathophysiology diagnosis and treatment Cerebral salt wasting CSW is a syndrome of hypovolemic hyponatremia caused by natriuresis and diuresis. Following the first clinical description of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion SIADH in 1957 such patients were assumed to develop hyponatremia from nonosmotic arginine vasopressin AVP secretion with.
However some authorities contend that CSW does not really exist and. Cerebral salt wasting CSW is another potential cause of hyponatremia in those with CNS disease particularly patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Exact aetiology is unclearincreased adrenergic activity increased natriuretic peptides increased perfusion pressure increased dopamine. CSW is characterized by hyponatremia and extracellular fluid depletion due to inappropriate sodium wasting in the urine 5. It has been reported in cases with subarachnoid haemorrhage 8 infections 7 head injury 9 brain tumours 10 trans-sphenoidal pituitary surgery 11 and neurosurgery. Cerebral salt wasting tends to resolve within weeks to months after onset but can remain a chronic issue. A vital clinical characteristic of patients affected by cerebral salt-wasting syndrome is that the aforementioned manifestations tend to respond positively to volume and sodium replacement.



































Posting Komentar untuk "Cerebral Salt Wasting Treatment"